Ghidra: The Open-Source Powerhouse for Reverse Engineering

Introduction
In the modern cybersecurity landscape, reverse engineering tools play a critical role in understanding how software behaves. Whether analyzing malware, testing software vulnerabilities, or studying legacy systems, professionals rely on reliable, transparent, and feature-rich platforms. One such remarkable tool is Ghidra, an open-source software reverse engineering (SRE) framework that empowers cybersecurity experts and researchers around the world.
Originally developed by the National Security Agency (NSA), this software framework made headlines when it was publicly released. Since then, it has become an essential utility in academic research, malware analysis, and software auditing — reshaping the boundaries of cybersecurity learning and development.
Key Features of Ghidra
The versatility of this tool lies in its comprehensive set of capabilities that cater to both beginners and professionals. Below is a table summarizing its most notable features and functionalities:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Disassembly | Converts machine code into human-readable assembly instructions. |
| Decompiler | Translates binary code into high-level language for easier understanding. |
| Cross-Platform Support | Runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux without major compatibility issues. |
| Scripting Support | Enables users to automate tasks using Java or Python scripting. |
| Collaboration Mode | Allows multiple analysts to work on the same project simultaneously. |
| Plugin Architecture | Users can add or develop custom plugins to extend functionality. |
| Graphical User Interface | Offers an intuitive GUI that simplifies complex analysis processes. |
| Open-Source Nature | Encourages transparency, security community contribution, and code auditing. |
Why Cybersecurity Experts Prefer It
Reverse engineering was once a domain reserved for government agencies and advanced research laboratories. However, the release of Ghidra changed this dynamic by offering professional-grade features for free.
Security researchers prefer it for several reasons:
- Cost Efficiency – Being open-source, it eliminates expensive licensing costs.
- Transparency – The public availability of its source code allows experts to verify and improve its algorithms.
- Comprehensive Analysis Tools – From binary decompilation to data flow tracking, it provides a full toolkit for reverse engineering.
- Community Support – A vibrant online community continuously develops plugins, tutorials, and learning material.
Additionally, many universities have integrated it into cybersecurity curriculums, allowing students to explore software behavior at the assembly level and understand how vulnerabilities are exploited.
How It Works
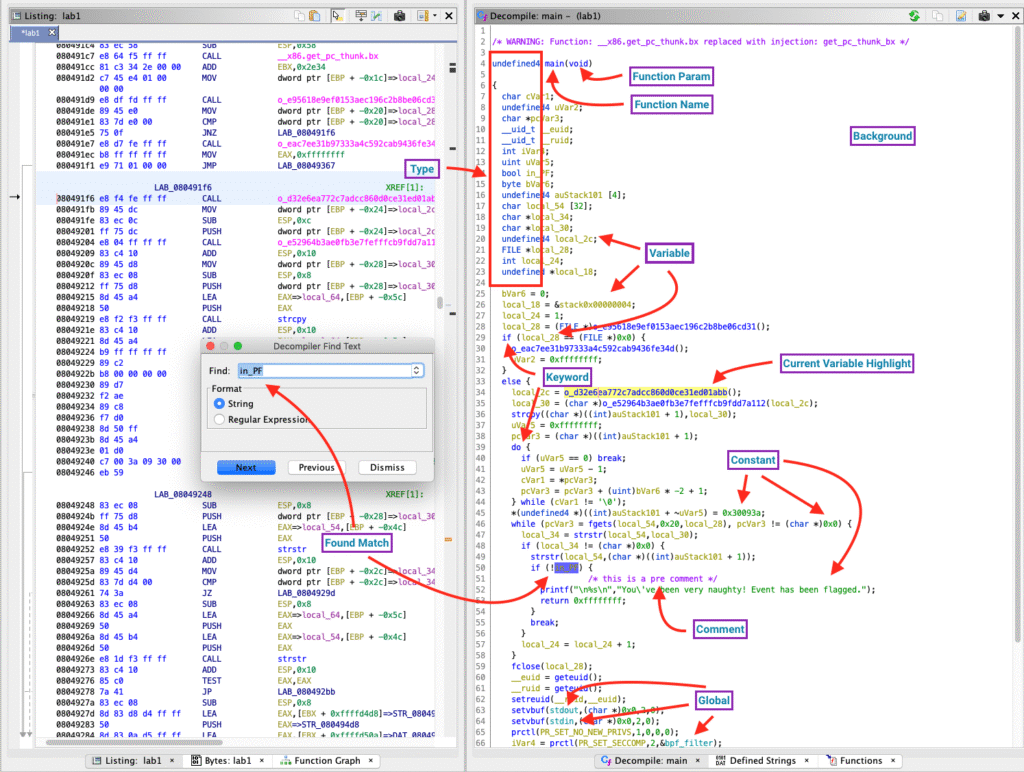
At its core, the framework performs static analysis — examining compiled code without executing it. It breaks down binaries into understandable representations like control-flow graphs, call hierarchies, and variable references. This helps security experts trace how a program manipulates data, interacts with memory, and executes system-level commands.
It supports numerous processor architectures including x86, ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, and more. With its modular design, analysts can import various file formats, making it ideal for inspecting executables from diverse operating systems.
Moreover, its decompiler is among the most powerful features — capable of transforming low-level machine instructions into C-like pseudocode. This enables faster understanding of malware or unknown applications without diving deep into assembly syntax.
Comparison with Other Reverse Engineering Tools
While several tools exist in the reverse engineering ecosystem, such as IDA Pro, Radare2, and Binary Ninja, the open-source advantage and flexibility make this tool highly attractive. Below is a comparative overview:
| Aspect | Ghidra | IDA Pro | Radare2 | Binary Ninja |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| License Type | Open-Source (Free) | Commercial (Paid) | Open-Source | Commercial (Paid) |
| Decompiler Included | Yes | Yes (Paid Plugin) | Partial | Yes |
| User Interface | Graphical + CLI | Graphical + CLI | Command-Line Focused | Graphical + CLI |
| Collaboration Tools | Yes | Limited | No | No |
| Customization | Extensive via Plugins | Moderate | High (Manual Setup) | Moderate |
From the table, it’s clear that the NSA-developed tool offers one of the most balanced combinations of performance, accessibility, and extensibility.
Educational and Practical Applications
Beyond professional cybersecurity labs, this software has become a staple in academic and research environments. Students studying computer science, information security, or software engineering use it to:
- Learn binary and assembly language structures.
- Study software vulnerabilities and exploit mechanisms.
- Conduct ethical malware analysis and sandbox testing.
- Analyze firmware or embedded systems.
In real-world applications, penetration testers and malware analysts rely on it to:
- Reverse-engineer suspicious executables.
- Validate software integrity.
- Identify hidden functionalities or backdoors.
- Reconstruct algorithms from compiled code.
Advantages and Limitations
Like any sophisticated tool, it offers tremendous advantages but also has a few limitations.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Free and open-source | Slightly steeper learning curve for beginners |
| Multi-platform compatibility | May consume more memory on large projects |
| Supports numerous architectures | Some features lag behind commercial alternatives |
| Active developer and research community | Requires manual configuration for complex analyses |
Despite these minor drawbacks, the benefits overwhelmingly outweigh the challenges, especially for professionals who need a cost-effective yet robust reverse engineering solution.
Future Developments and Community Impact
Since its public release, the open-source community has actively contributed to improving the tool’s efficiency, performance, and usability. Frequent updates, community plugins, and documentation expansion ensure that it remains competitive with paid tools.
As cybersecurity threats evolve, frameworks like this will continue to help analysts uncover hidden code behavior, prevent data breaches, and safeguard digital infrastructure. The educational impact has been equally profound — introducing thousands of students to the world of reverse engineering without financial barriers.
Conclusion
Ghidra has transformed the landscape of software reverse engineering by combining accessibility, power, and transparency. It bridges the gap between academic learning and professional analysis while promoting global collaboration in cybersecurity.
Whether you’re a security researcher, ethical hacker, or student exploring software internals, this platform provides a solid foundation for understanding how digital systems operate at their core. Its open-source ethos and continuous development ensure that it will remain a cornerstone tool in the cybersecurity domain for years to come.
Read more: Ghidralite: Comprehensive Guide to Ghidra Reverse Engineering Tool